Oxygen therapy manufacturer: 6 fatal diseases you can treat with
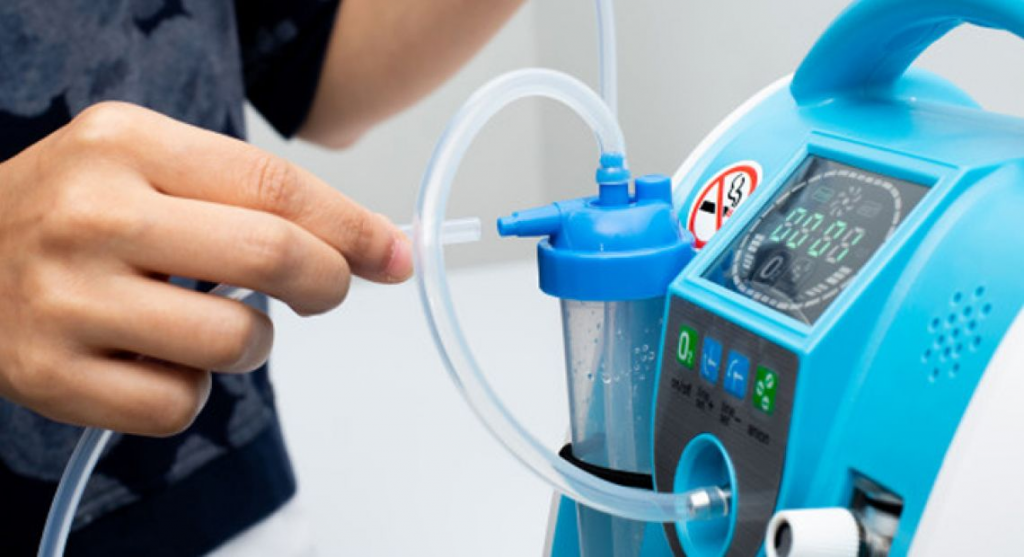

Oxygen therapy manufacturer considers that the oxygen concentrator is part of your important equipment: much more advantageous than oxygen cylinders. it can be good to use:
- either to administer oxygen to an animal lacking it, via a mask, tracheal intubation or in an oxygen cage for oxygen therapy
- either as part of gas anesthesia
In both cases, the oxygen concentrator has considerable advantages over the use of oxygen cylinders:
- no risk of explosion
- no need to always have bottles in stock or recommend frequently.
- It is a reliable, robust and easy to use device.
BUT HOW DOES IT WORK?
Oxygen therapy manufacturer also tells the operating principle of an oxygen concentrator good to use in a veterinary clinic is very simple: the device sucks in the ambient air (composed of approximately 20% oxygen and 80% nitrogen), and passes it under high pressure by a filter which traps nitrogen molecules. This is a zeolite (a crystal) filter, and since a filter saturates quickly, it needs to be cleaned.
Think of a vacuum cleaner dust filter, which needs to be cleaned regularly for the vacuum to work! This is why an oxygen concentrator consists of two filters, which work alternately to ensure a continuous flow of concentrated oxygen: one is cleaned by the machine while the second takes over and vice versa.
WHY THEN MIGHT A CONCENTRATOR NEED TO BE TESTED?
Oxygen therapy manufacturer says that a new concentrator produces 90-95% concentrated oxygen. But over time, a large number of saturation and cleaning cycles eventually deteriorate the filters, even if the device has two.
As most of the devices available on the market do not have a built-in oxygen concentration tester, it is impossible to know after a certain time whether the oxygen supplied by your concentrator is still 95% pure. 80%, 50% or even less!
The oxygen deficit causes a slowdown in cell activity. Thus, the oxygen deficit can manifest itself in particular by:
- Reduced physical possibilities (shortness of breath on exertion (dyspnea), fatigability)
- Morning headaches
- Cough
- Cyanosis: purplish, bluish color in the extremities (nails, ears, lips)
- Edemas
- Abnormal drowsiness
- Almost permanent respiratory congestion or recurrent bronchitis with difficulty in recovery translate into difficulty in bronchial drainage .
Oxygen therapy: treatment of respiratory failure
The oxygen therapy manufacturer provides treatment of hypoxia (insufficient oxygenation of tissues) due to respiratory failure. It allows the oxygen enrichment of the inspired air.
The oxygen is good to use both on a temporary basis, in acute conditions, that prolonged and daily basis in chronic conditions. People with respiratory failure returning to their homes may benefit from short or long term oxygen therapy.
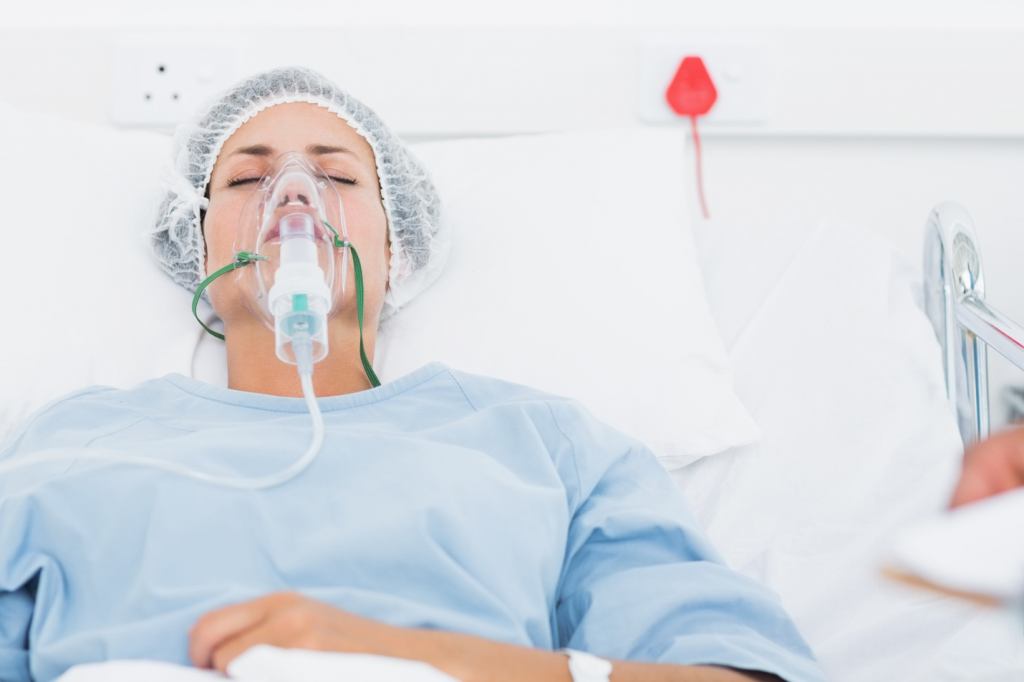
The solutions offered for home oxygen therapy are stationary and portable oxygen concentrators, gaseous oxygen cylinders and liquid oxygen tanks.
Oxygen concentrators
The fraction of inspired oxygen, which is 21% in atmospheric air, can thus be increased to almost 100% with an oxygen concentrator designed by oxygen therapy manufacturer. Until the advent of "high flow" oxygen concentrators (up to 9 L / min), liquid oxygen was the only source available at these flow rates.
Today, traveling under oxygen with its concentrator is possible under certain conditions.
Principle and operation of an oxygen concentrator
Generally, the oxygen concentrator is a device for concentrating and filtering oxygen from the air. Still noisy for some, it is advisable by oxygen therapy manufacturer to use a tubing extension to get away from the concentrator. Moreover, we can distinguish two types of concentrators: fixed or portable.
Precautions for using an oxygen concentrator
Oxygen is a colorless, odorless and tasteless gas (not detectable). Similarly, it is an oxidizer: it maintains combustion and thus exposes to the risk of fire and explosion.
General precautions are to avoid combustible materials:
- Greasy substances: beware of dirty hands, do not lubricate the concentrator, similarly, do not apply creams and ointments to the patients' faces.
- Combustible gases: lacquers, deodorants, storage of propane or butane nearby, ...
- Volatile products: solvent, alcohol, gasoline, paint, etc.
Some safety rules:
Oxygen therapy manufacturer gives some rules to follow for the safety purpose. We have discussed here.
- BAsically, never smoke with your oxygen and do not smoke in the room where your source is easy to install.
- Similarly, Don't cook on your oxygen
- In addition, Keep the oxygen concentrator in a dry, clean and ventilated place in an upright position
- Furthermore, Keep the equipment away from any source of heat: fireplace, candle, stove, radiator, ...
- Moreover, Do not put anything on your oxygen concentrator
- Simultaneously, Do not wear the portable concentrator under clothing.
- Do not store the device in a passageway, in a damp room, in a kitchen or in a cupboard.
Fixed oxygen concentrators
The fixed hubs are in the form of a piece of furniture on casters weighing 14 to about 25 kg. Oxygen therapy manufacturer designed these to use 24 hours a day. They plug into the mains and consume around 300 watts (and almost 500 watts for "high speed").
Portable oxygen concentrators
The portable oxygen concentrators promote ambulation respiratory impairment. The operation of these hubs is similar to that of fixed hubs. They nevertheless have a dual power supply, mains and internal batteries.
The volume of oxygen that they are able to produce per minute is limited to 3 L. Their autonomy depends on the battery, the oxygen therapy mode (pulsed or continuous) and the flow rate setting.
The battery is the most important element of the concentrator because without it: no mobility! The autonomy can go from 3 to 5 hours and can double from 6 to 10 hours with additional batteries.
Oxygen therapy manufacturer explains that the portable oxygen concentrators weigh between 2 and 10 kg. The lighter ones can be easily transported using a shoulder bag like the Inogen one G3 or the Platinum mobile.
Oxygen delivery devices
These devices allow the transmission of oxygen concentrated by the device to the patient. Among these connections, we can distinguish:
The oxygen scope:
The nasal cannula is a simple, reliable and generally well tolerated delivery device. However, wearing an oxygen glasses can cause unpleasant friction on the skin, especially behind the ears and consequently cause irritation or burns. Ear protectors for oxygen glasses are important to deal with this inconvenience.
The oxygen mask:
Oxygen therapy manufacturer provides it to cover the nose, the mouth. The oxygen mask, however, hinders communication, eating and coughing. It is even uncomfortable for some patients (feeling of oppression).
The tubing extension:
It allows oxygen-dependent people to widen their walking perimeter with their oxygen concentrator. It requires the use of a universal fitting. The connector comes between the tubing of the glasses or oxygen mask and the extension which will connect directly to the concentrator.





